Popular Tips
YOU MIGHT BE INTERESTED IN
Car Exhaust System Explained - Parts, Design, Construction, Working & more
by Jatin Chhibber |
19/03/2021
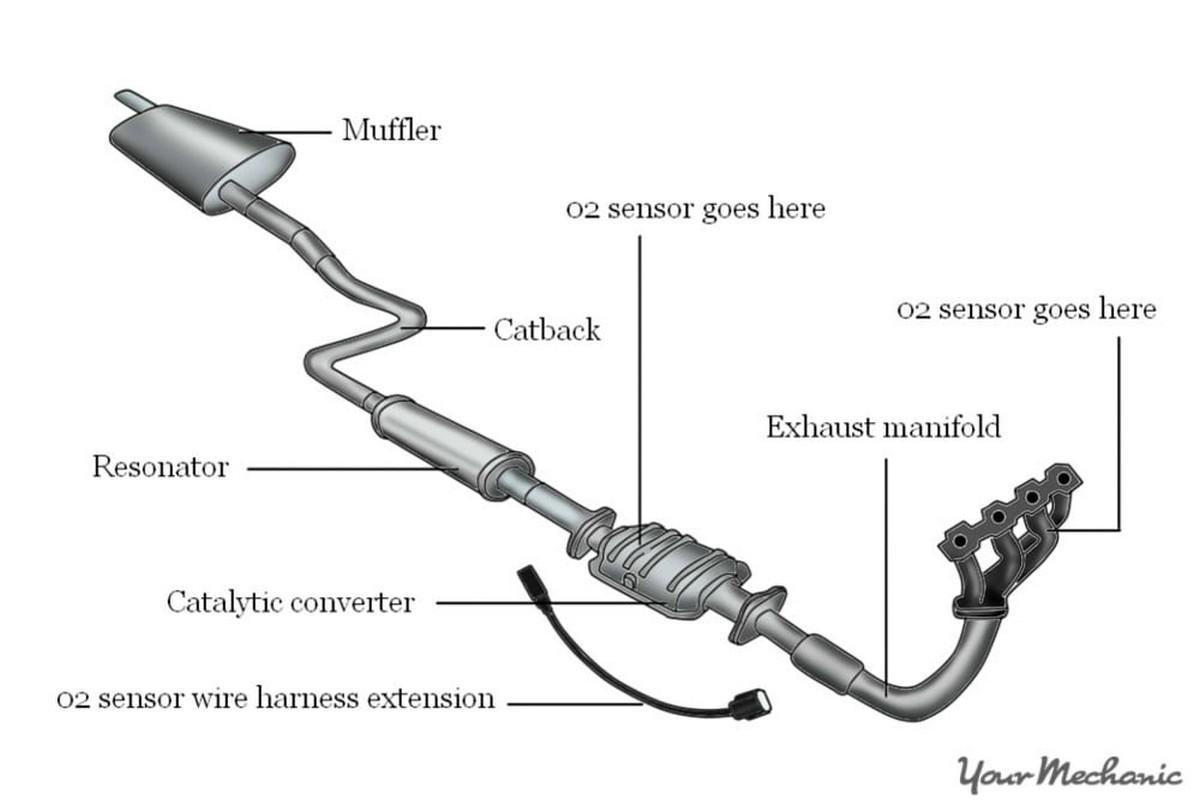
Here are all the components of an exhaust system and how they work. It consists of four main components namely- O2 Sensor, Catalytic Converter, Resonator and Muffler.
- Tag:
- car engine
- exhaust smoke









 Follow us on google news
Follow us on google news
